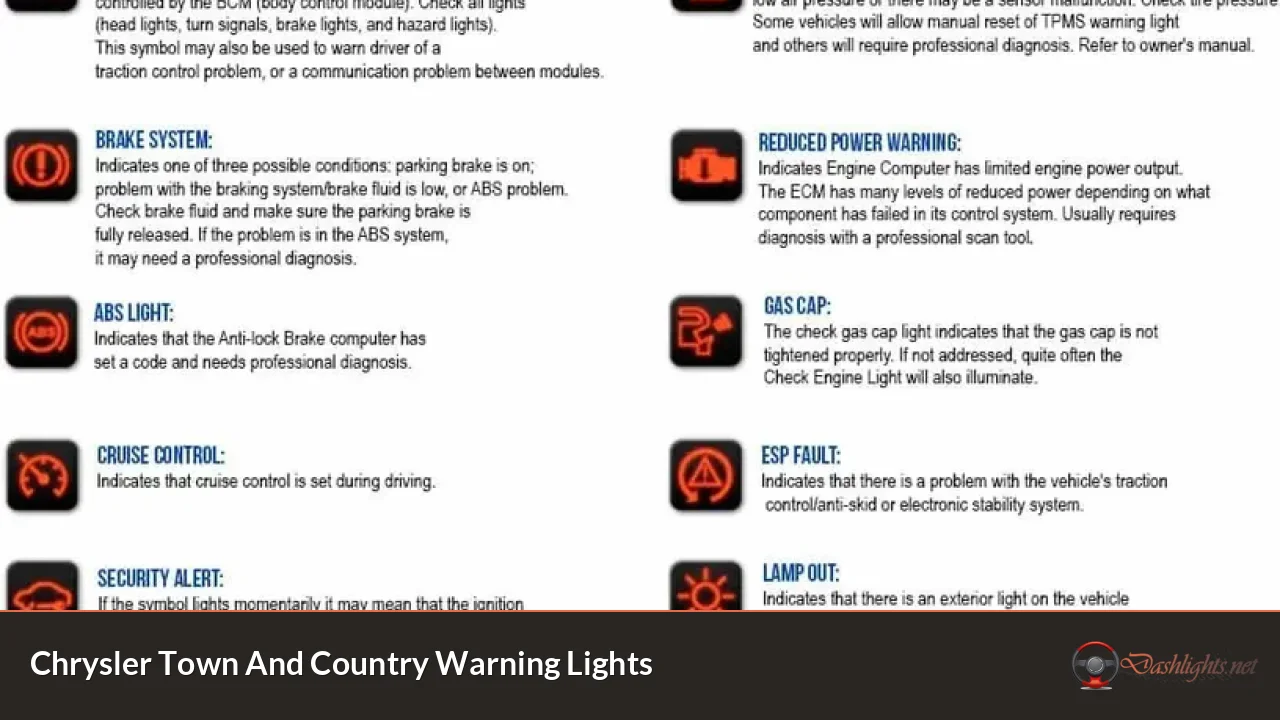
Understanding the Importance of Warning Lights in Modern Vehicles
Warning lights are essential features in modern vehicles, acting as the primary communication tool between your car and you. These lights serve as indicators of various vehicle conditions and performance metrics, directly impacting both safety and maintenance. Ignoring these warnings could lead to serious mechanical failures, unintended safety hazards, or even significant repair costs down the line. For instance, when a warning light, such as the Check Engine light, illuminates, it signals that the onboard diagnostics have detected an issue that requires attention. Understanding what these warning lights mean can help you maintain your vehicle's health and ensure your safety on the road.
Warning Light Overview
The "Check Engine" light, often represented by an engine silhouette illuminated in yellow or amber, is one of the most common warning lights. When this light appears on your dashboard, it indicates that the engine control unit (ECU) has detected a malfunction in the engine system or related components. The yellow color signifies that the issue is less urgent than a red warning light; however, it still requires prompt attention. Ignoring the Check Engine light for an extended period could lead to more serious problems, affecting vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
Possible Causes
When the Check Engine light comes on, it can indicate a variety of issues. Here are the top five common reasons:
-
Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The oxygen sensor monitors the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust. A malfunction can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
-
Loose or Damaged Gas Cap: If the gas cap isn’t sealed properly, it can cause fuel vapors to escape and trigger the warning light, indicating an evaporative emissions system leak.
-
Bad Mass Air Flow Sensor: This sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine to optimize the air-fuel mixture. A faulty sensor can disturb engine performance.
-
Failing Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter reduces toxic emissions. If it's failing, you may notice poor acceleration and reduced fuel efficiency.
-
Spark Plug or Wires Issues: Worn-out spark plugs can misfire, resulting in a rough engine idle and poor performance, causing the Check Engine light to activate.
-
Engine Thermostat Failure: A malfunctioning thermostat may cause the engine to run too hot or cold, leading to potential damage and triggering the warning light.
Associated Systems
The Check Engine light is mostly related to the engine's performance and emissions systems, including:
-
Fuel System: Affected by issues with fuel injectors, pumps, or filters, which play critical roles in delivering the right fuel mixture.
-
Exhaust System: Includes the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors that monitor emissions and help maintain efficiency.
-
Ignition System: Comprises components such as spark plugs and ignition coils that are vital for engine starting and smooth operation.
These systems interact closely; for example, a failing mass air flow sensor might lead to insufficient fuel delivery, resulting in poor combustion and increased emissions. Problems in one area can exacerbate issues in others, so it’s vital to diagnose and treat the root cause as soon as the warning light appears.
Diagnostic Steps
Diagnosing issues related to the Check Engine light involves several steps:
-
Utilizing OBD-II Scanners: Start by connecting an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port. This will read error codes stored in the ECU that relate to the Check Engine light.
-
Interpreting Error Codes: Note the codes displayed on the scanner; looking them up can give you insight into the specific issues affecting your engine.
-
Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of engine components that relate to the identified fault codes. Check wires, hoses, and sensors for any visible damage or wear.
-
Testing Components: Use a multimeter to measure the performance of sensors and components. For example, check the resistance of spark plugs and the signal from the mass air flow sensor.
-
Performing Functional Tests: If necessary, perform functional tests on relevant systems to pinpoint specific failures, such as checking for proper fuel pressure.
-
Documenting Findings: Keep a record of all diagnostic steps, findings, and tests performed for future reference and warranty purposes.
Recommended Actions
If the Check Engine light illuminates, here’s what you should do:
-
Immediate Steps: Safely pull over to a parking area and turn off the engine. If the light is steady, you may be able to continue driving to a service station. If it’s flashing, stop immediately; this indicates a severe engine misfire that can cause significant damage.
-
Consult Your Owner’s Manual: Your vehicle’s owner’s manual will provide specific guidance on the warning light and any immediate actions you should take.
-
Monitoring Performance: Pay close attention to how your vehicle responds after the warning light appears. If you experience unusual noises, changes in handling, or performance deficits, seek professional help.
Potential Repairs
Addressing the issues associated with the Check Engine light can involve a variety of repairs:
-
oxygen sensor replacement: This typically costs between $100 to $300, including parts and labor.
-
Gas cap replacement: If a loose or damaged gas cap is the issue, this is a simple and inexpensive fix, generally costing less than $100.
-
Mass airflow sensor repairs: Replacing a faulty mass airflow sensor can range from $300 to $600.
-
Catalytic converter replacement: This is more expensive, usually between $1,000 to $2,500, depending on the make and model.
While some repairs can be conducted by a DIY owner with moderate mechanical skills, others, especially those related to the exhaust system, are best left to professionals.
Preventive Measures
To avoid triggering the Check Engine light, consider these preventive measures:
-
Regular Maintenance: Adhere to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule, which includes oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug inspections.
-
Monitor Fuel Quality: Use the correct fuel type and avoid low-quality options that might lead to engine performance issues.
-
Check for Recalls or Services Campaigns: Stay updated on any recalls or service campaigns relevant to your vehicle.
-
Observe Early Warning Signs: Pay attention to any unusual noises, decreased performance, or unusual odors. Doing so can help you catch potential problems early.
Common Misconceptions
Here are some frequent misconceptions about the Check Engine light:
-
Myth: The Check Engine light means I need an oil change: This is incorrect; while low oil pressure could trigger a warning, the Check Engine light indicates a more complex issue.
-
Myth: If the light goes off, the problem is fixed: Just because the light turns off doesn’t mean the issue has been resolved; it often means the ECU has temporarily reset but may activate again.
-
Myth: I can ignore the Check Engine light: Ignoring this light can lead to significant long-term damage and more expensive repairs.
Final Words
The Check Engine light is a crucial component of modern vehicle diagnostics, serving as a reminder for car owners to remain vigilant about their vehicle's health. Ignoring it could lead to severe consequences, affecting performance, efficiency, and safety. It's vital for vehicle owners to take these warnings seriously, consult their owner’s manuals, and seek professional assistance when necessary. Regular maintenance and awareness of your vehicle’s systems can help you avoid the onset of problems that trigger the dreaded warning light. Prioritize your vehicle’s health to ensure a safe and enjoyable driving experience.